Versatile Nature of Carbon
Versatile Nature of Carbon: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Versatile Nature of Carbon, Bonding of Carbon with Heteroatoms, Tetravalency of Carbon, Multiple Bond Formation by Carbon, Catenation Property of Carbon, Compounds of Carbon, Saturated Hydrocarbons, etc.
Important Questions on Versatile Nature of Carbon
The suffix used for naming an aldehyde is
The molecular formula of the first member of certain group of organic compounds is . What will be the name and molecular formula of the third member of this group if the members of this group are in homologous series.
IUPAC name of the compound is:
Choose the correct molecular formula and structural formula of an alkene having five carbon atoms:
The first member of alkane that shows structural isomerism is:
The functional groups present in propanol and propanal respectively are:
Identify the structural isomers of pentane.
What is the general formula of alkane.
To complete the following flowchart, the compounds needed to be filled in the blanks respectively are:
The structural formula of marsh gas is:
The molecular formula of the compounds in a homologous series are . The suitable general formula for the given compounds is:
An example of a saturated hydrocarbon is:
The IUPAC name of the following compound is:
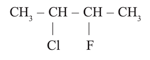
The property of an element to bond with itself through covalent bonds to form a chain or ring is called:
In alkyl halides, the homologous series of alkyl halide is represented as:
Which of the following compounds are alkenes?
Which of the following statements are correct for covalent compounds?
Identify the unsaturated compounds from the following.
Select the characteristics of isomers.
Which of the following hydrocarbons are alkanes?
